
What Is the Average Car Loan Payment? Rates, Terms & Smart Savings Tips
When you’re in the market for a vehicle, understanding what others pay each month can help you budget more effectively. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or looking to upgrade, knowing the typical monthly car payment amount gives you a realistic baseline for what to expect.
Keep reading to learn about current average car loan payments, the factors that influence your monthly cost and practical strategies to lower your payment.
Key Takeaways
- The average car loan payment varies significantly between new and used vehicles, with new cars requiring substantially higher monthly payments
- Longer auto loan terms lower your monthly payment but increase the total interest you’ll pay over time
- A larger down payment reduces both your monthly payment and the amount of interest charged throughout the loan
- Shopping around for the best rate and considering refinancing options can save you thousands over the life of your loan
What Is the Average Car Loan Payment?
According to Experian’s Q3 2025 data, the average monthly payment for a new vehicle is $748, while used car buyers pay an average of $532 per month. These figures represent a steady upward trend, with new car payments increasing 1.8% from the prior year and used car payments rising 1.5% year-over-year, according to an analysis from LendingTree. The amount financed for new cars has also climbed, sitting at approximately $2,000 higher in 2025 compared to 2024 and 2023 levels, per Bankrate.
The difference between average car payments for new vs. used cars stems from several factors. New vehicles cost more upfront, which means larger loan amounts even with comparable down payments and terms. Additionally, new cars often come with longer loan terms, though this doesn’t always translate to lower monthly payments, given the higher purchase price.
These averages give you a benchmark for evaluating your own situation. If you’re looking at monthly payments significantly higher than these figures, it might be worth reassessing your budget, the vehicle you’re considering or the loan terms being offered. On the flip side, if your payment comes in well below average, you’re likely in a strong financial position with good credit and favorable loan terms.
Which Factors Influence Car Loan Payments?
Several key variables work together to determine what you’ll pay each month for your vehicle. Understanding how each factor impacts your payments helps you make informed decisions when buying a car. Consider the following:
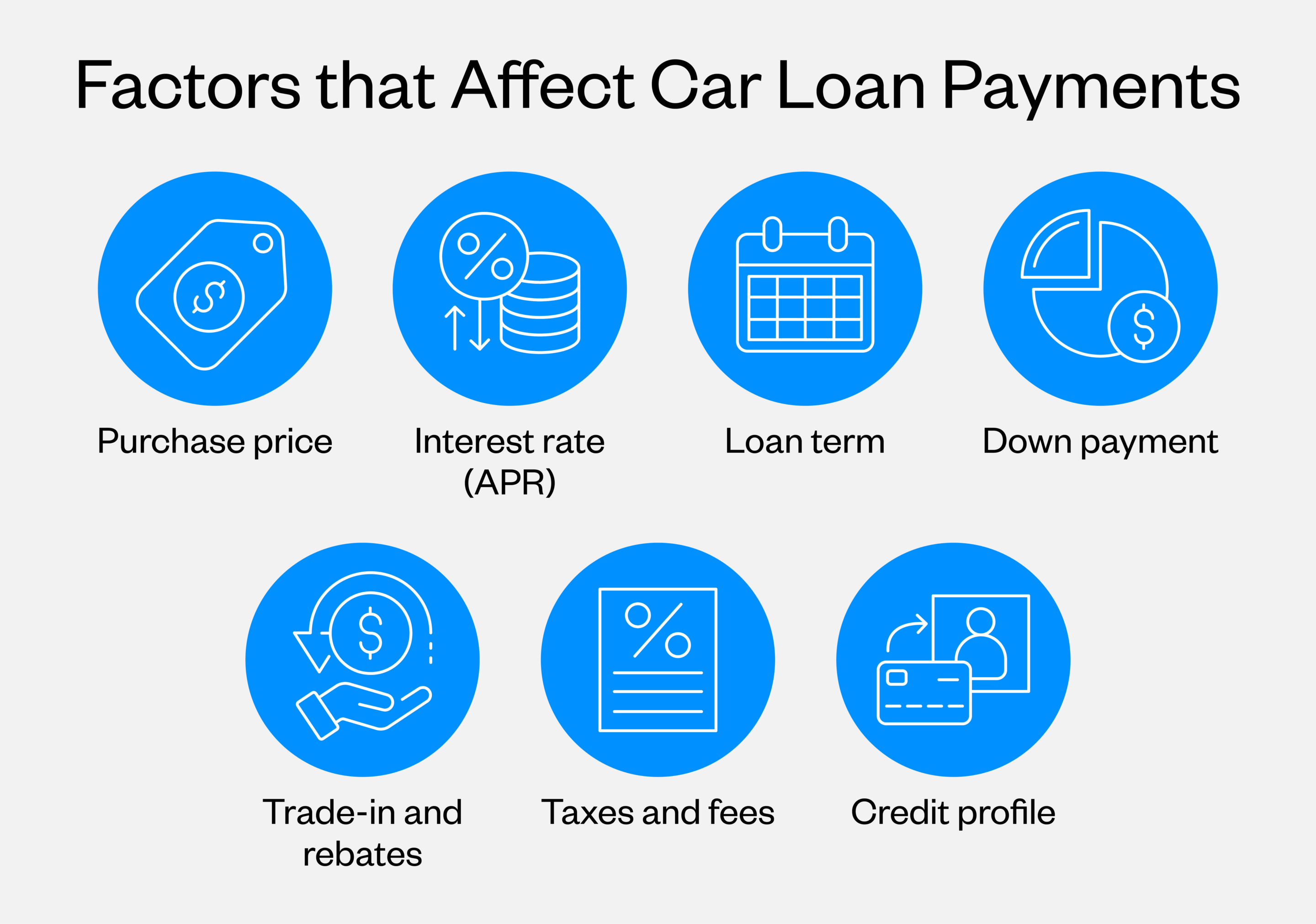
Purchase price
The purchase price is the sticker price of the car, and is the main factor that influences your car loan payment. A $30,000 vehicle will naturally require higher monthly payments than a $20,000 one, assuming all other factors are equal. Using a car affordability calculator before you start shopping can help you set realistic expectations.
Interest rate (APR)
Your annual percentage rate (APR) directly affects how much extra you’ll pay beyond the vehicle’s purchase price. Average car loan interest rates currently range from around 5% for borrowers with good credit to over 20% for those with poor credit. Even a difference of two or three percentage points can add thousands of dollars to your total cost over the life of the loan.
Loan term
Standard car loan term lengths typically range from 36 to 72 months, with some lenders offering terms as long as 84 months. While stretching your payments over six or seven years lowers your monthly obligation, you’ll pay significantly more in interest.
Down payment
Putting more money down at purchase reduces your loan amount and, consequently, your monthly payment. A substantial down payment also helps you avoid owing more than your car is worth if its value depreciates quickly.
Trade-in and rebates
If you have a vehicle to trade in, its value gets applied to your purchase, reducing the amount you need to finance. Similarly, manufacturer rebates and incentives lower your effective purchase price. Both can have a meaningful impact on your monthly payment by decreasing your loan principal.
Taxes and fees
Sales tax, registration fees, documentation charges and other costs get added to your loan amount unless you pay them upfront. These expenses vary by state and can add several thousand dollars to what you’re financing. Some buyers forget to account for these when calculating their expected payment.
Credit profile
Your credit score is one of the most influential factors in determining your interest rate. Average car payment by credit score varies dramatically. However, borrowers with scores above 720 typically qualify for the best rates, while those below 600 typically face substantially higher costs. Lenders view your credit history as an indicator of how likely you are to repay the loan as agreed.
How to Lower Your Car Loan Payment
You have more control over your car payment than you might think. These strategies can help you secure better terms and keep your monthly costs manageable:

- Improve your credit before applying: Spending a few months working on building good credit before you apply for financing can save you significant money. Pay down existing debt, make all payments on time and avoid opening new credit accounts. Even moving from fair credit to a good credit score can reduce your interest rate by several points
- Increase your down payment: The more cash you put down, the less you’ll need to borrow. If you can manage it, aim for 20% down on your new car or 10% on a used one. This lowers your monthly payment and helps you build equity faster. Consider saving for a larger down payment rather than rushing into a purchase with minimal money down
- Shop for better interest rates: Don’t accept the first rate you’re offered. Consider offers from banks, credit unions and online lenders before signing anything. Comparing a bank vs. a credit union, you might find that credit unions provide more competitive rates. Additionally, getting auto loan pre-approval can give you negotiating power at the dealership
- Consider a shorter term: If you can comfortably afford higher monthly payments, choosing a shorter term saves you money on interest. A 48-month loan costs less overall than a 72-month loan, even though the monthly payment is higher
- Refinance later: If you’re stuck with a high interest rate now, you’re not locked in forever. Once you’ve improved your credit or if market rates drop, refinancing a car loan can lower your monthly payment or shorten your term. Many lenders offer auto loan refinancing options that can save you hundreds over the remaining life of your loan
- Consider add-ons carefully: Dealerships offers a variety of additional products to protect or enhance your vehicle. Adding additional options may increase the overall financed amount which impacts your monthly payment. Evaluate each add-on carefully and don’t be pressured into purchases that strain your budget
Average Car Loan Payments and How to Keep Yours Affordable
Understanding the average car loan payment helps you set realistic expectations, but your actual payment depends on the choices you make during the financing process. By improving your credit, shopping around for competitive rates and choosing loan terms that fit your budget, you can secure a payment that works for your financial situation.
California Credit Union offers competitive auto loan rates to help you get behind the wheel of your next vehicle. Whether you’re wondering how to get a car loan for the first time or looking to refinance your current vehicle, our team can guide you through the process and find solutions that keep your monthly payments manageable.





