
Car Lease vs Buy Calculator
Deciding whether to lease or buy a car can be challenging because there are so many factors to consider, ranging from financial implications to individual preferences and driving needs. Using our Car Lease vs. Buy Calculator helps you cut through the confusion and make a decision based on your actual budget and needs.
Auto Buying Center
When you're ready, visit our Auto Buying Center and take advantage of our trusted partners that can help find the perfect new or used vehicle for you. They can help negotiate prices, provide recommendations and even deliver the vehicle to you. You can also get pre-approved for an auto loan.
What are the main differences between leasing and buying a car?

The main difference between buying and leasing a car is ownership. Both buying and leasing have monthly payments if you use a loan to purchase your vehicle. However, you typically have higher monthly payments when buying a car because you’re paying off the full purchase price. And when you buy a car and own it, you’re responsible for all repairs and regular maintenance. On the other hand, leasing includes all warranty coverage, including routine maintenance.
What are the pros of buying a car?
Buying a car comes with many benefits. Eventually, after paying off the loan, you’ll own the vehicle, which means having a significant investment. Other benefits of buying a car include the following:
- Ability to build equity: When you own your car, you can build equity by making regular monthly payments on your loan. Then, the value of your car is an asset you can sell or trade in
- Customization: Buying a car means owning it, allowing you to customize it any way you like
- No mileage restrictions: When you purchase a car, there’s no limit on how often you can drive it
- Lower long-term cost: Buying a car typically offers long-term savings even though the upfront costs are higher than leasing because you eventually own the car once it’s paid off
If you decide to purchase a new or used vehicle, take advantage of our competitive auto loan rates.
What are the cons of buying a car?
Of course, buying a car isn’t the best option for everyone. Potential drawbacks of buying a car include the following:
- Higher upfront costs: Buying a car comes with higher upfront costs because you may need to pay a percentage of the purchase price as a down payment on the loan
- Higher monthly payments: In addition to higher upfront costs, buying a car typically comes with higher monthly payments because you’ll pay the entire cost of the purchase price
- Depreciation: Car value decreases as soon as you drive it off the lot. The older the car, the less valuable it is
- Maintenance and repair costs: When you buy a car, you’re responsible for all maintenance and repair costs
If you’re considering buying a car, use our Vehicle Payments Calculator to determine how much you’ll pay monthly.
What are the pros of leasing a car?
Leasing a car is a better option for some individuals. The benefits of leasing a car include the following:
- Lower upfront costs: Leasing also typically comes with lower upfront costs and doesn’t require a down payment
- Ability to drive a newer vehicle: When you lease a vehicle, you can drive a newer one because you don’t have to pay the purchase price, making it more affordable to drive a new vehicle
- Flexibility: Leasing terms are flexible, and you can even modify the lease of your lease, mileage limit and other terms to suit your needs
- Limited maintenance and repair costs: The warranty typically covers most maintenance and repair costs when you lease a car
What are the cons of leasing a car?
A few of the cons of leasing a car include the following:
- Inability to build equity: When you lease a vehicle, you don’t own it, so you can’t build equity as you make payments
- Limited customization: Since you never own a leased car, you won’t be able to make any modifications
- Mileage restrictions: Leases may come with mileage restrictions that prevent you from driving them too frequently
- Potential fees and charges: If you exceed your mileage restrictions, you may face hefty fees when your lease ends
What is the cost comparison over time for leasing vs. buying a car?
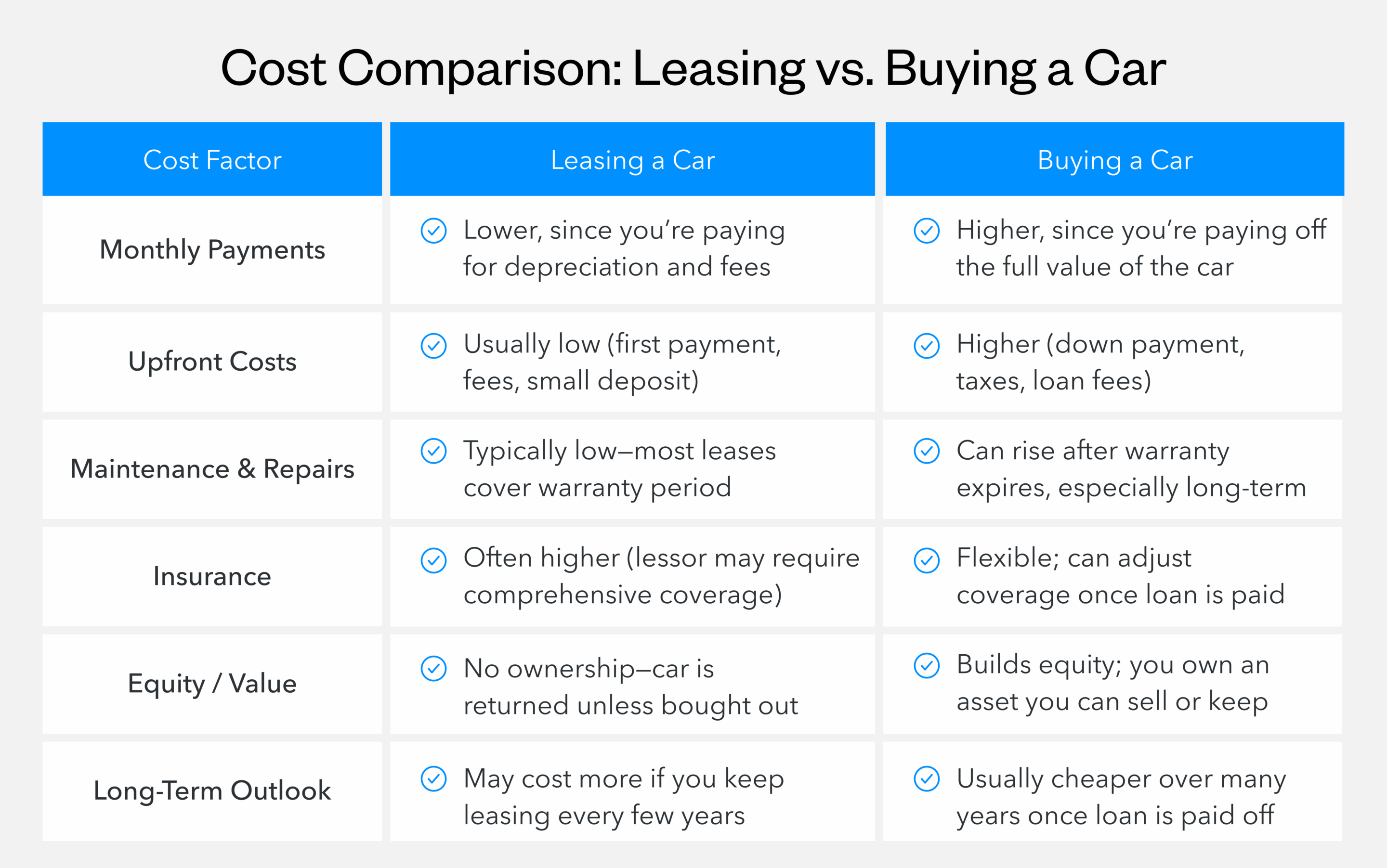
- Monthly payments: Auto lease payments are typically lower than purchase payments because you're only covering the vehicle's depreciation during your lease term. Purchase payments are higher since you're paying toward owning the entire vehicle, but these payments eventually end once the loan is paid off
- Upfront costs: Leasing often requires less money at signing, sometimes just the first month's payment and a security deposit. Buying usually demands a down payment ranging from 10%-20% of the purchase price, plus taxes, registration and dealer fees
- Maintenance and repairs: Leased vehicles typically stay under warranty for the entire lease term, keeping your repair costs minimal. Owned vehicles require you to budget for maintenance and repairs, especially after the warranty expires
- Insurance: Both options require comprehensive coverage, but lease agreements often mandate higher coverage limits and lower deductibles. This can make insurance slightly more expensive for leased vehicles compared to older owned cars
- Resale or end value: When you own a car, you capture any remaining value through trade-in or private sale. With leasing, you simply return the car with no equity gained, though you also avoid the hassle and uncertainty of selling
- Long-term cost outlook: Over five to seven years, buying often costs less total money if you keep the vehicle after paying off the loan. Leasing costs less per year but never stops, making it more expensive if you continuously need a vehicle. If you already own a vehicle but want to lower your payments, refinancing an auto loan might help reduce your monthly costs
Wrapping up: Should I lease or buy a car?
The decision to lease or buy a car comes down to your driving habits, personal preferences and financial situation. Neither option is universally better, as they both serve different needs and lifestyles.
The benefits of a credit union extend beyond just competitive rates – you'll work with a financial institution that prioritizes your success over profit margins. When you're ready to move forward with your vehicle decision, we're here to support you with transparent terms and personalized guidance.
When you're ready, you can also visit our Auto Buying Center and take advantage of our trusted partners that can help find the perfect new or used vehicle for you. They can help negotiate prices, provide recommendations and even deliver the vehicle to you!
California Credit Union cannot and does not guarantee the accuracy or the applicability to your individual circumstances. All examples are hypothetical and are for illustrative purposes. Calculator results are estimates based on information you provided and California Credit Union does not guarantee your ability to receive these terms. We encourage you to seek personalized advice from qualified professionals regarding all personal finance issues.







